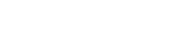Arthritis is a prevalent condition that affects millions of seniors worldwide. It is crucial for both seniors and their caregivers to have a comprehensive understanding of arthritis to effectively manage the condition and improve the quality of life. This article aims to provide an overview of arthritis, including its symptoms, causes, and various treatment options available for seniors.
What is Arthritis?

Arthritis is a general term used to describe inflammation and stiffness in the joints. It is not a single disease but rather a group of conditions that affect the joints and surrounding tissues. The most common types of arthritis that affect seniors are osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, gout, and psoriatic arthritis. Each type has its unique characteristics and requires different approaches to treatment.
Symptoms of Arthritis in Seniors

The symptoms of arthritis in seniors can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. The most common symptoms include joint pain, stiffness, swelling, and reduced range of motion. Seniors with arthritis may also experience fatigue and general discomfort. It is essential to recognize these symptoms early on to seek appropriate medical intervention.
Causes and Risk Factors

Arthritis in seniors can be attributed to various factors. Age-related changes in joints, such as the breakdown of cartilage, are commonly observed in osteoarthritis. Genetic factors also play a role in certain types of arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis. Previous joint injuries, obesity, and excess weight can contribute to the development of arthritis. Other factors like infections, hormonal imbalances, and autoimmune disorders can also increase the risk of arthritis in seniors.
Diagnosing Arthritis in Seniors
Diagnosing arthritis in seniors involves a combination of physical examination, medical history assessment, imaging tests, and laboratory tests. During a physical examination, the healthcare professional will assess the affected joints for tenderness, swelling, and range of motion. They may also ask about the patient’s medical history and perform imaging tests such as X-rays or MRIs to evaluate the condition of the joints. Laboratory tests, such as blood tests or joint fluid analysis, may be conducted to rule out other potential causes of joint symptoms.
Treatment Options
The treatment of arthritis in seniors aims to alleviate pain, reduce inflammation, and improve joint function. There are several treatment options available, including medications, physical therapy, assistive devices, lifestyle modifications, alternative therapies, and surgical interventions. Medications commonly prescribed for arthritis include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), and corticosteroids. Physical therapy and exercise programs can help improve joint mobility and strengthen surrounding muscles. Assistive devices like canes or braces may be recommended to support joint function. Lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a healthy weight and managing stress, can also play a crucial role in managing arthritis. In some cases, surgical interventions like joint replacement or arthroscopy may be necessary.
Managing Arthritis in Daily Life

Seniors with arthritis can take several steps to manage the condition and minimize its impact on their daily lives. Balancing rest and activity is essential to prevent overexertion and manage pain. Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce stress on the joints, while applying heat or cold therapy can help alleviate discomfort. Protecting joints during daily tasks, such as using proper ergonomics and assistive devices, can prevent further damage. Additionally, managing stress and prioritizing mental health can contribute to overall well-being.
Support and Resources for Seniors with Arthritis

Seniors with arthritis should not hesitate to seek support from healthcare professionals and specialists who can provide guidance and expertise in managing the condition. Support groups and community organizations can also be valuable resources, as they offer a platform for seniors to connect with others facing similar challenges and share experiences. Additionally, there are numerous online resources and information available that provide educational materials, self-help tips, and updates on the latest advancements in arthritis treatment. Accessible exercise programs designed specifically for seniors with arthritis can also be beneficial, as they provide guidance on safe and effective exercises to improve joint function and overall fitness.
Preventive Measures and Promoting Joint Health

While arthritis is a complex condition, there are steps seniors can take to reduce the risk of developing arthritis or slow its progression. Maintaining an active lifestyle is crucial, as regular exercise helps keep joints flexible and strengthens the muscles around them. Engaging in low-impact activities like swimming, walking, or cycling can be particularly beneficial for seniors with arthritis. Eating a balanced diet that includes anti-inflammatory foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and omega-3 fatty acids, can also contribute to joint health. Protecting joints during physical activities by using proper techniques, equipment, and avoiding excessive strain can help prevent injuries that may lead to arthritis. Lastly, seniors should prioritize regular check-ups and screenings to detect any potential joint issues early on.
Understanding arthritis is vital for seniors and their caregivers to effectively manage the condition and maintain a good quality of life. By recognizing the symptoms, understanding the causes and risk factors, and exploring the available treatment options, seniors can take proactive steps to alleviate pain, improve joint function, and manage arthritis effectively. It is essential to consult healthcare professionals for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan. With proper care, support, and lifestyle modifications, seniors with arthritis can continue to lead active, fulfilling lives. Remember, early detection and management of arthritis are key to minimizing its impact and maximizing overall well-being.